Chest fat and gynecomastia are two conditions that are often confused with one another. Chest fat, also known as pseudogynecomastia, is the accumulation of excess fat tissue in the chest area, resulting in a more feminine appearance. Gynecomastia, on the other hand, is the enlargement of breast tissue in men due to an imbalance of hormones. While both conditions can affect men, they have different causes and require different treatments.
Importance of Understanding the Difference between Chest Fat and Gynecomastia
It’s important to understand the difference between chest fat and gynecomastia because the treatment options for each condition are different. While chest fat can often be reduced through exercise and diet, gynecomastia typically requires medical intervention. Additionally, the psychological impact of each condition can also differ. Men with chest fat may feel self-conscious about their appearance, while men with gynecomastia may experience anxiety or depression due to the feminisation of their chest.
Brief Overview of the Article
In this article, we will explore the differences between chest fat and gynecomastia. We’ll discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for each condition, as well as lifestyle changes and surgical options that can help reduce their appearance. We’ll also touch on the psychological impact of each condition and provide tips for coping with the emotional side effects.
II. Chest Fat
A. Definition of Chest Fat
Chest fat, also known as pseudogynecomastia, is a condition in which the chest area of a man accumulates excess fat tissue. The chest may appear to be enlarged and more feminine in appearance. Unlike gynecomastia, which is caused by an imbalance of hormones, chest fat is not related to hormonal changes.
B. Causes of Chest Fat
The causes of chest fat can vary from person to person, but are often related to lifestyle factors. Some common causes include:
1. Sedentary lifestyle: A lack of physical activity can lead to an increase in body fat, including chest fat.
2. Poor diet: Consuming a diet high in processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats can contribute to the development of excess body fat.
3. Genetics: Some people may be predisposed to developing chest fat due to their genetic makeup.
4. Hormonal imbalances: While less common than in gynecomastia, hormonal imbalances can contribute to the development of chest fat in some cases.
C. Symptoms of Chest Fat
The primary symptom of chest fat is the appearance of excess tissue in the chest area. This can manifest as a soft, fleshy mound or a more firm, fibrous mass. The chest may appear enlarged or saggy, and some men may experience tenderness or discomfort in the chest area.
D. Treatment Options for Chest Fat
1. Exercise and diet: The most effective way to reduce chest fat is through a combination of exercise and diet. Cardiovascular exercise, such as running or cycling, can help burn calories and reduce overall body fat, while strength training exercises can help tone the chest muscles and improve the appearance of the chest area. A balanced diet that includes plenty of lean protein, fruits and vegetables, and healthy fats can also help reduce overall body fat and improve overall health. To have some motivation for exercise, read How to Stay Motivated for Exercise
2. Liposuction: In some cases, medical intervention may be necessary to reduce the appearance of chest fat. Liposuction can be used to remove excess fat tissue from the chest area. This is a surgical procedure that involves the insertion of a small tube under the skin to suction out fat. While liposuction can be effective in reducing chest fat, it is important to note that it is a surgical procedure and carries risks and potential complications.
3. CoolSculpting: This is a non-surgical treatment option that uses a cooling device to freeze and destroy fat cells in the chest area. This treatment can be effective in reducing the appearance of chest fat, but may require multiple sessions to achieve optimal results.
E. Prevention of Chest Fat
Preventing chest fat can be achieved through a combination of lifestyle changes. Maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise can help reduce the risk of developing excess fat tissue in the chest area. Limiting alcohol intake and avoiding smoking can also help reduce the risk of developing chest fat, as these habits have been linked to increased body fat and decreased muscle mass.
III. Gynecomastia
A. Definition of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia is a medical condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in men. The condition is caused by an imbalance of hormones, particularly an increase in estrogen levels or a decrease in testosterone levels.
B. Causes of Gynecomastia
The causes of gynecomastia can vary, but they are often related to hormonal imbalances. Some common causes include:
1. Puberty: During puberty, hormone levels fluctuate, and gynecomastia is a common occurrence in many adolescent boys. The condition often resolves on its own within a few months to a year.
2. Aging: As men age, their testosterone levels naturally decrease, while their estrogen levels may remain stable, leading to the development of gynecomastia. For Tips to increase your testosterone levels naturally, read I Need More Testosterone for My Manhood
3. Medications: Certain medications, such as anti-androgens, anabolic steroids, and some antidepressants, can cause gynecomastia as a side effect.
4. Health conditions: Certain health conditions, such as liver disease, thyroid problems, and testicular tumours , can cause hormonal imbalances that lead to the development of gynecomastia.
C. Symptoms of Gynecomastia
The primary symptom of gynecomastia is the enlargement of breast tissue in men. The breasts may feel tender or sore, and the nipple may be sensitive or swollen. In some cases, men may experience discharge from the nipple.
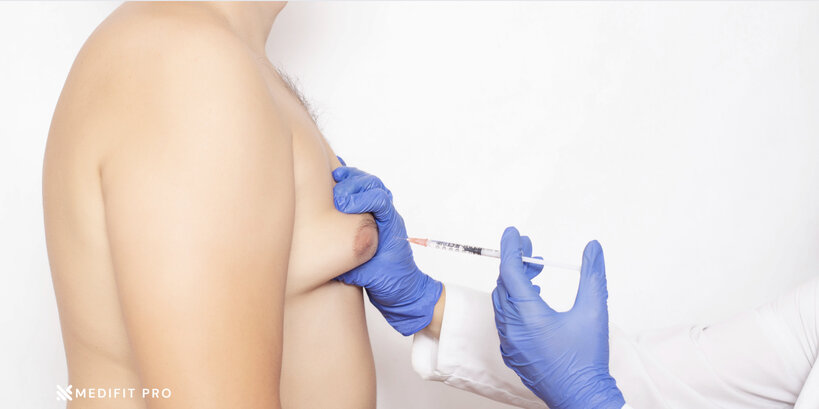
D. Treatment Options for Gynecomastia
1. Observation: In many cases, gynecomastia may resolve on its own without any medical intervention. It is important to monitor the condition and seek medical advice if it persists or becomes more severe.
2. Medications: Certain medications, such as tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors, can be used to block the effects of estrogen and reduce the size of breast tissue in men.
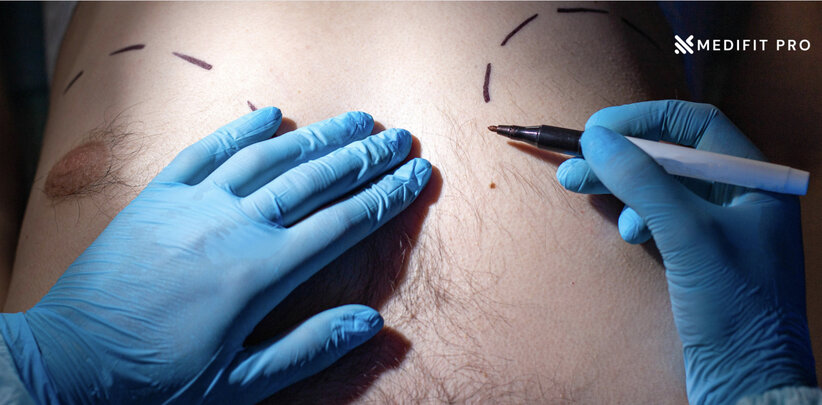
3. Surgery: In cases where gynecomastia is severe or does not respond to other treatments, surgery may be necessary to remove excess breast tissue. This is typically done under general anesthesia and involves the removal of glandular tissue and/or fat tissue from the breast area.
E. Prevention of Gynecomastia
Preventing gynecomastia can be difficult, as the condition is often related to hormonal imbalances that are beyond an individual’s control. However, avoiding the use of anabolic steroids and other medications that can cause hormonal imbalances can help reduce the risk of developing gynecomastia. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, may also help reduce the risk of hormonal imbalances and gynecomastia. For more knowledge, you can also read Habits and foods that Sabotage Your Testosterone Levels
IV. Diagnosis
A. How to Determine if You Have Chest Fat or Gynecomastia
It can be difficult to differentiate between chest fat and gynecomastia, as the symptoms and appearance can be similar. However, there are some key differences to consider.
Chest fat is typically more diffuse and affects the entire chest area, while gynecomastia is characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in a more localized area around the nipple. Gynecomastia may also feel tender or sore, while chest fat does not usually cause discomfort.
If you are unsure whether you have chest fat or gynecomastia, it is recommended that you consult with a medical professional.
B. Diagnostic Tests for Gynecomastia
If you suspect that you have gynecomastia, your doctor may recommend a variety of diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis and rule out any underlying medical conditions.
1. Physical Examination: Your doctor will perform a physical exam to evaluate the size and shape of your breasts and to check for any discharge from the nipple.
2. Blood Tests: Blood tests may be performed to evaluate your hormone levels and to rule out any underlying medical conditions that could be causing gynecomastia.
3. Imaging Tests: Imaging tests, such as a mammogram, may be recommended to evaluate breast tissue and rule out any other conditions, such as breast cancer.
C. Medical Professionals to Consult With
If you suspect that you have chest fat or gynecomastia, it is recommended that you consult with a medical professional. Your primary care physician may be able to provide an initial evaluation and refer you to a specialist if necessary.
Some medical professionals who specialize in the treatment of chest fat and gynecomastia include:
1. Endocrinologists: These medical professionals specialize in the treatment of hormonal imbalances and may be able to diagnose and treat gynecomastia.
2. Plastic Surgeons: Plastic surgeons may be able to provide surgical treatment options for gynecomastia, such as liposuction or breast reduction surgery.
3. Oncologists: If imaging tests or other diagnostic tests reveal the possibility of breast cancer, an oncologist may be consulted to provide further evaluation and treatment.
Diagnosing chest fat or gynecomastia may require a combination of physical exams and diagnostic tests. It is recommended that you consult with a medical professional to confirm the diagnosis and rule out any underlying medical conditions. Medical professionals who specialize in the treatment of chest fat and gynecomastia include endocrinologists, plastic surgeons, and oncologists.
V. Diet and Exercise Tips to Reduce Chest Fat
A. Introduction
While there is no guaranteed way to spot-reduce chest fat, incorporating diet and exercise changes into your lifestyle can help to reduce overall body fat, including chest fat. Additionally, these changes can improve overall health and well-being.
B. Diet Tips
1. Reduce Caloric Intake: Consuming fewer calories than your body burns in a day can lead to weight loss, including in the chest area. Consider reducing portion sizes or consuming low-calorie, nutrient-dense foods.
2. Eat Whole Foods: Whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains, can help to reduce overall body fat and improve overall health.
3. Limit Processed Foods: Processed foods, such as sugary snacks and fried foods, can contribute to weight gain and should be limited or avoided.
4. Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help to flush toxins from the body and improve overall health.
C. Exercise Tips
1. Strength Training: Incorporating strength training exercises, such as push-ups and bench presses, can help to build muscle in the chest area and improve overall body composition.
2. Cardiovascular Exercise: Cardiovascular exercise, such as running or cycling, can help to burn overall body fat, including chest fat.
3. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): HIIT workouts, which involve short bursts of high-intensity exercise followed by periods of rest, can help to burn calories and improve overall fitness.
D. Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Gynecomastia
1. Avoid Hormone Disrupting Chemicals: Certain chemicals, such as those found in plastic bottles and food packaging, can disrupt hormone balance and contribute to gynecomastia. Avoiding these chemicals by using glass containers and buying organic food can help to reduce the risk of gynecomastia.
2. Manage Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as liver or thyroid disease, can contribute to gynecomastia. Managing these conditions through medication or lifestyle changes can help to reduce the risk of gynecomastia.
3. Avoid Anabolic Steroids: Anabolic steroids, which are often used to enhance athletic performance, can disrupt hormone balance and contribute to gynecomastia. Avoiding these substances can help to reduce the risk of gynecomastia.
Incorporating diet and exercise changes into your lifestyle can help to reduce chest fat and improve overall health. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as avoiding hormone-disrupting chemicals, managing underlying medical conditions, and avoiding anabolic steroids can help to reduce the risk of gynecomastia. As always, consult with a medical professional before making any significant changes to your diet or exercise routine.
VI. Surgery
A. Surgical Options for Chest Fat
While diet and exercise can often help to reduce chest fat, in some cases, surgery may be necessary to achieve the desired results. Some surgical options for chest fat include:
1. Liposuction: Liposuction is a surgical procedure that involves removing excess fat from the body using a suction device. It can be used to remove excess fat from the chest area and create a more defined chest.
2. Breast Reduction Surgery: Breast reduction surgery, also known as reduction mammoplasty, is a surgical procedure that involves removing excess breast tissue and skin to create a more proportionate chest.
B. Surgical Options for Gynecomastia
1. Liposuction: Liposuction can also be used to treat gynecomastia by removing excess breast tissue and fat from the chest area.
2. Mastectomy: In more severe cases of gynecomastia, a mastectomy may be necessary. This procedure involves removing all breast tissue from the chest area.
3. Hormonal Therapy: In some cases, hormonal therapy may be used to treat gynecomastia by regulating hormone levels in the body.
C. Risks and Considerations
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks and considerations to take into account when considering surgery for chest fat or gynecomastia. Some potential risks of surgery include infection, bleeding, scarring, and complications related to anesthesia. It’s important to discuss these risks with a qualified medical professional before undergoing any surgical procedure.
Additionally, surgery is often considered a last resort and should only be pursued after other options, such as diet and exercise or hormonal therapy, have been exhausted.
The Psychological Impact
A. The psychological impact of chest fat and gynecomastia
Chest fat or gynecomastia is a common medical condition that affects men of all ages. It refers to the enlargement of the breast tissue in men, resulting in the appearance of breasts. This condition can be caused by various factors such as hormonal imbalances, certain medications, and obesity. While it is not a life-threatening condition, it can have a significant impact on a man’s psychological well-being.
Men with chest fat or gynecomastia often experience feelings of shame, embarrassment, and self-consciousness. They may avoid social situations and activities that require them to take off their shirts, such as swimming or going to the beach. Some men may even feel like they are less of a man or have lost their masculinity because of their condition.
The psychological impact of chest fat and gynecomastia can also affect a man’s romantic relationships. Men with this condition may feel less confident and attractive to their partners, which can lead to difficulties in intimacy and communication. They may also feel like their condition is a burden on their partners, leading to feelings of guilt and inadequacy.
Additionally, men with chest fat or gynecomastia may experience negative self-talk and body shaming. They may constantly compare themselves to other men with a more masculine physique, leading to feelings of insecurity and dissatisfaction with their bodies.
B. Coping strategies for individuals with chest fat or gynecomastia
If you are a man with chest fat or gynecomastia, it is important to know that you are not alone. There are many coping strategies that can help you manage the psychological impact of this condition.
1. Seek medical treatment: The first step in coping with chest fat or gynecomastia is to seek medical treatment. Your doctor can determine the underlying cause of your condition and recommend appropriate treatment options, such as medications or surgery.
2. Practice self-care: Engage in activities that make you feel good about yourself, such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies. Take care of your body by eating a healthy diet and getting enough sleep.
3. Challenge negative thoughts: Notice negative thoughts and self-talk, and challenge them with positive affirmations. Focus on your strengths and accomplishments, rather than your perceived flaws.
4. Seek support: Reach out to friends, family members, or a support group for men with chest fat or gynecomastia. Talking to others who have experienced similar challenges can be a helpful source of support and validation.
5. Embrace your body: Accepting and embracing your body as it is can be a powerful coping strategy. Practice self-compassion and focus on the things you like about yourself, rather than fixating on your perceived flaws.
In this article, we discussed the psychological impact of chest fat and gynecomastia, including how it can affect a man’s social life and relationships. We also provided coping strategies for men with this condition, such as seeking medical treatment, practicing self-care, challenging negative thoughts, seeking support, and embracing their bodies.
Reference
Mayo Clinic. (2022). Gynecomastia. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gynecomastia/symptoms-causes/syc-20351793
























Recent Comments